The concept of the normal force is a fundamental aspect of physics that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of objects on inclined planes. As we delve into this topic, we will explore how the normal force acts on objects positioned at various angles on an inclined surface. This force is essential for calculating other forces acting on the object, influencing its motion and stability. Whether you are a student learning about physics or a curious individual seeking to understand the principles behind inclined planes, grasping the normal force is key to mastering this subject.
The normal force is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical implications in real-world applications. From the design of roads and ramps to the construction of buildings and bridges, understanding the normal force can lead to safer and more efficient engineering solutions. By examining how this force varies with different angles and weights, we can gain insights into how objects interact with their surroundings and why certain materials are chosen for specific purposes.
In this article, we will answer crucial questions about the normal force on inclined planes, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential force. We will also discuss various scenarios, equations, and practical examples that illustrate the significance of the normal force in everyday life. So, let’s embark on this journey to uncover the mysteries of the normal force and its implications on inclined planes!
What is the Normal Force on an Inclined Plane?
The normal force is defined as the perpendicular force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it. When an object is placed on an inclined plane, the normal force acts perpendicular to the surface of the incline. This force is crucial in determining how the object behaves under the influence of gravity and other forces.
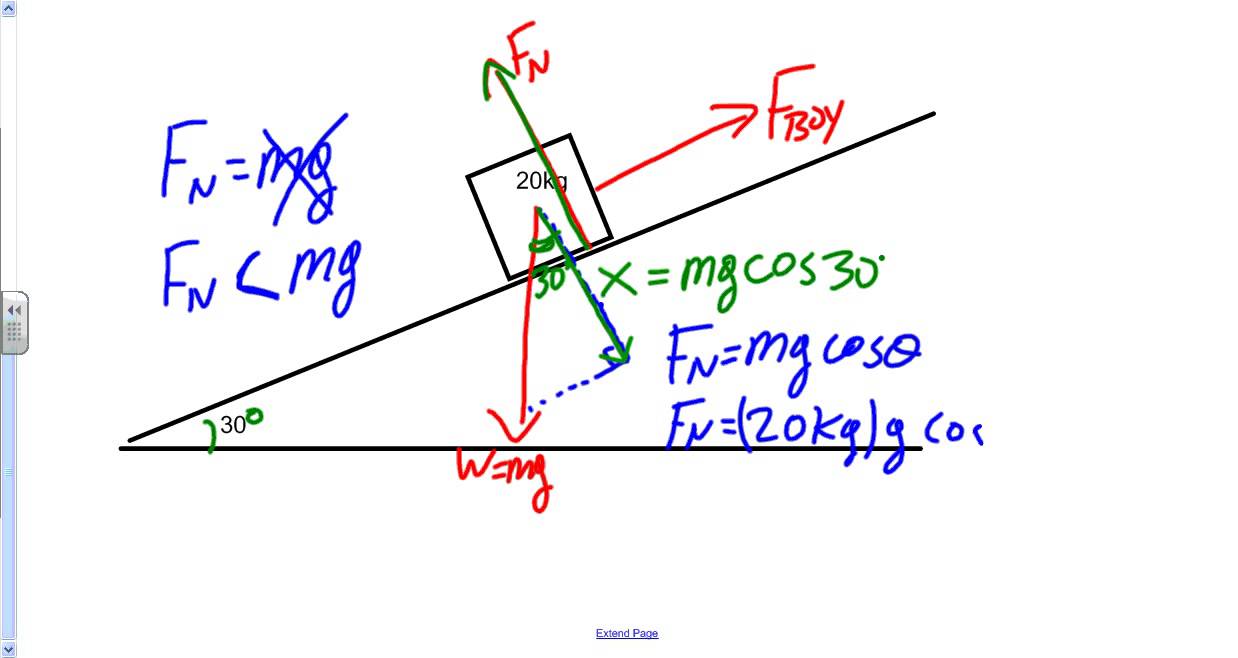
How is the Normal Force Calculated on an Inclined Plane?
Calculating the normal force on an inclined plane involves understanding the forces acting on the object. The weight of the object can be broken down into two components: one parallel to the incline and one perpendicular to it. The normal force can be calculated using the following formula:
- Normal Force (N) = Weight (W) * cos(θ)
Where:
- Weight (W) = mass (m) * gravitational acceleration (g)
- θ = angle of the incline
What Factors Affect the Normal Force on an Inclined Plane?
Several factors can influence the normal force on an inclined plane:
- The angle of the incline (θ): As the angle increases, the normal force decreases.
- The mass of the object (m): A heavier object will exert a greater normal force.
- The presence of friction: Frictional forces can alter the effective normal force experienced by the object.
Why is the Normal Force Important in Physics?
The normal force is essential for understanding various physical phenomena, including motion, stability, and equilibrium. It plays a significant role in determining how objects behave when subjected to different forces, making it a crucial concept in mechanics. By analyzing the normal force, we can predict how objects will respond to external forces, informing both theoretical studies and practical applications.
How Does Friction Relate to the Normal Force on an Inclined Plane?
Friction is directly related to the normal force. The frictional force can be calculated using the formula:
- Frictional Force (f) = Coefficient of Friction (μ) * Normal Force (N)
Where:
- Coefficient of Friction (μ) varies depending on the materials in contact.
As the normal force changes due to variations in the incline angle, the frictional force will also change, impacting the object's motion.
What are Real-Life Applications of Normal Force on Inclined Planes?
Understanding the normal force on inclined planes has numerous real-life applications, including:
- Designing ramps for accessibility.
- Analyzing vehicle dynamics on hilly roads.
- Engineering structures that can withstand different loads.
- Sports science, particularly in activities like skiing and snowboarding.
Can the Normal Force be Zero on an Inclined Plane?
Yes, the normal force can be zero in certain scenarios, such as when an object is in free fall or when the incline is at a specific angle where the component of gravity parallel to the incline equals the gravitational pull. In these cases, the object may lose contact with the surface, leading to a state of free motion.
How Does the Angle of the Incline Affect the Normal Force?
As the angle of the incline increases, the normal force decreases. This is because a greater portion of the object’s weight acts parallel to the incline, reducing the perpendicular force exerted on the surface. Understanding this relationship is crucial for engineers and physicists when designing systems that involve inclined planes.
Conclusion
In summary, the normal force on inclined planes is a vital concept in physics, influencing how objects interact with surfaces at angles. By comprehending the factors that affect the normal force, including angle, mass, and friction, we can better predict the behavior of objects in various scenarios. This knowledge not only enhances our understanding of physics but also informs practical applications in engineering, sports, and everyday life.
You Might Also Like
Karaoke Games For Switch: Sing Your Heart Out Anywhere!Understanding The Troubles Behind The Direct Express App
Discovering The Allure Of McDonald's In St. Michael, MN
The Prime Rib DC: A Culinary Gem In The Heart Of The Capital
Discovering The Regal Edwards Greenway Grand Palace: A Cinematic Experience Like No Other
Article Recommendations
- Political Parties Of The Presidents
- President Of United States Job Description
- Presidential C
- Show A Picture Of The United States
- Tallest President Of The Us
- President Of Usa Website
- How Old Id Trump
- The American Presidents Series
- How Does Someone Become President Of The United States
- Presidential Winning